Compounding chemotherapy refers to the customized preparation of chemotherapy drugs tailored to meet the specific needs of individual patients. This process is crucial for adjusting dosages, combining drugs, or creating formulations that are not commercially available. In the United States, compounding chemotherapy plays a significant role in cancer treatment, especially in pediatric oncology, rare cancers, and cases requiring personalized dosing.
Market Overview
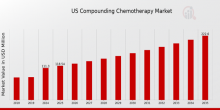
The US compounding chemotherapy market is steadily expanding, driven by the increasing incidence of cancer, the growing need for personalized medicine, and advances in sterile compounding techniques. Compounded chemotherapy drugs are prepared under stringent regulatory conditions to ensure safety, sterility, and precision in dosage.Market Drivers
- Rising Cancer Prevalence: The increasing number of cancer diagnoses across the US is significantly boosting the demand for tailored chemotherapy solutions.
- Growing Demand for Personalized Medicine: Compounded chemotherapy supports individualized treatment plans, which are becoming more common in modern oncology practices.
- Technological Advancements: Improved compounding equipment and automation are enhancing the safety, accuracy, and efficiency of chemotherapy preparation.
- Hospital and Specialty Pharmacy Growth: The rise in specialty pharmacies and hospital-based compounding facilities is improving access to customized chemotherapy drugs.
- Regulatory Support: Stricter regulations from organizations like the USP (United States Pharmacopeia) are improving the quality and standardization of compounded chemotherapy drugs, increasing trust in their use.
Market Challenges
- Regulatory Complexity: Compliance with USP <797> and <800> guidelines for sterile compounding and hazardous drug handling can be costly and challenging for smaller facilities.
- Risk of Contamination: Compounded chemotherapy drugs require extremely high standards of sterility; lapses can lead to serious patient safety risks.
- High Operational Costs: Investment in cleanrooms, compounding equipment, and skilled pharmacists drives up the cost of compounding chemotherapy.
- Workforce Shortage: The need for highly trained compounding pharmacists and technicians is creating a workforce gap in the industry.
Recent Developments
- Increased automation in compounding facilities to reduce manual errors and improve safety.
- Growing adoption of closed-system transfer devices (CSTDs) to protect healthcare workers from hazardous drug exposure.
- Enhanced regulatory inspections and enforcement to ensure compliance with safety standards.
- Expansion of partnerships between hospitals and compounding pharmacies to streamline chemotherapy preparation.